Diabetes is a burgeoning health challenge that affects millions worldwide. This silent epidemic requires proactive measures for early detection and management. Here’s where diabetes screening tests come into play. Taking charge through these screenings can significantly mitigate associated health risks by detecting diabetes early when it’s more manageable. This practice not only curbs potential complications but also broadens the path to better health and quality of life for those at risk.
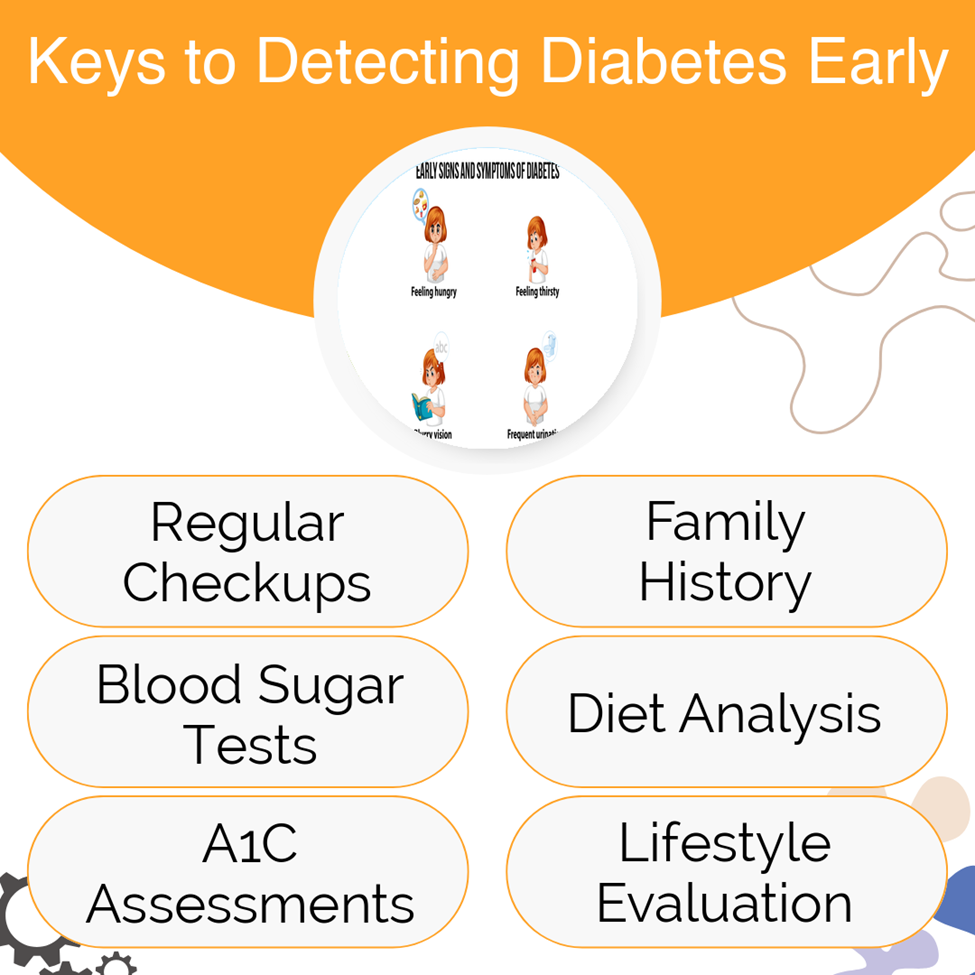
Recognizing Diabetes: The Silent Risk Factor
Understanding diabetes involves recognizing its various forms: Type 1, Type 2, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 relies heavily on insulin therapy, while Type 2 is often linked to lifestyle factors. Prediabetes serves as a warning sign, indicating rising blood glucose levels poised to tip into Type 2 diabetes if left unchecked. Gestational diabetes may occur during pregnancy and resolve post-delivery but raises the risk for future Type 2 diabetes.
The silent nature of diabetes means individuals can remain undiagnosed for years because symptoms are subtle or absent, and this is why regular screening is so vital. An undiagnosed condition can sneak up and unleash severe health problems like cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, or even kidney failure. Without intervention, the outcomes for untreated diabetes can be dire. Early identification through diabetes screening tests empowers individuals by fostering timely lifestyle and dietary changes, ultimately staving off these severe consequences.
The Essential Role of Diabetes Screening Tests
Who needs to undergo diabetes screening? Adults over 45 years, or younger individuals with risk factors such as obesity or family history, should consider regular screening. Early diabetes detection through these tests offers significant benefits, chief among them being improved health outcomes. The timely adoption of lifestyle changes guided by these tests can substantially delay or prevent the onset of diabetes.
Diabetes screening tests are cost-effective. By catching the disease early, these tests ultimately save on extensive treatment expenses later. National guidelines advocate for these screenings even when individuals feel fine because symptoms can be deceptive. Don’t wait for symptoms to manifest; embrace the reassurance and better health outcomes that come with regular screenings.
Decoding Diabetes Screening Tests
Understanding the variety of diabetes screening tests available helps in choosing the right one. The A1C test measures your blood sugar level over a few months, while the fasting blood sugar (FBS) test requires a fasting state to determine your glucose baseline. Another option, the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), measures your body’s ability to manage glucose after ingestion.
Here’s what these tests entail: – A1C Test: This provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It doesn’t require fasting, making it a convenient screening option. – Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Requires fasting overnight, then checking your blood sugar item. It mainly focuses on the fasting blood sugar levels. – Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This process involves fasting and then drinking a sugar solution. Blood sugar levels are then measured at multiple intervals to track glucose management.
For symptomatic individuals, random glucose tests are available to spot-check your blood glucose level. Each test offers a window into your glucose metabolism, essential for regular diabetes screening and the prevention of long-term complications.
Making Sense of Diabetes Screening Results
Interpreting these test results can pinpoint where you stand on the diabetes spectrum. For instance, normal fasting blood sugar levels should range between 70-99 mg/dL. Prediabetes falls between 100-125 mg/dL, while diabetes is diagnosed at 126 mg/dL or higher.
So, what if your screening results are positive?
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Discuss your results to understand your condition and the next steps.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Focus on a balanced diet with low sugar intake and regular exercise.
- Continuous Monitoring: Track your progress through future tests and remain vigilant about your health status.
Taking actionable steps ensures that a diagnosis isn’t the end but a new beginning towards better health management, guided by your healthcare team.
Disproving Diabetes Myths and Encouraging Action
Many myths deter people from undergoing diabetes screening tests. One misconception is that only overweight individuals need testing. However, factors like genetics can also elevate risk. Cost concerns also keep some away, yet these tests are often covered by insurance or available cost-effectively through wellness centers.
Another fear is the potential “life-changing” results, deterring tests. However, identifying diabetes early dramatically enhances quality of life, avoiding severe complications. Therefore, embracing early detection is key.
Here’s the bottom line: mitigating misconceptions, acknowledging the necessity of testing, and understanding the profound benefits of early detection and intervention can transform your health journey—ensuring diabetes and the importance of diabetes screening tests are part of your preventive health toolbox. Addressing fears and taking proactive steps is the most effective pathway to diabetes prevention and long-term health.
Don’t Let Diabetes Go Undetected
The Silent Risk Deserves a Loud Response.
Millions live with undiagnosed diabetes, unaware of the slow damage it causes to the heart, kidneys, nerves, and vision. Whether it’s Type 1, Type 2, prediabetes, or gestational diabetes, early detection through routine screening tests can change your health story.
What Your Numbers Mean
- Normal: FBS 70–99 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: FBS 100–125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: FBS 126+ mg/dL
If you’re over 40, overweight, have a family history, or even mild symptoms—don’t wait.
Common Screening Tests
A1C Test – Average sugar over 2-3 months, no fasting needed
Fasting Blood Sugar – Measures sugar after 8–10 hours of fasting
️ OGTT – Measures how your body handles sugar intake over time
️ Random Glucose Test – Instant check if you’re showing symptoms
Worried You Might Be at Risk?
Book Your Diabetes Screening at Standard Diagnostics Today!
Affordable, accurate, and accessible testing options available.
🩺 Your health. Your choice. Start with Standard.